READ: Basic Nervous System Anatomy
| Site: | Mountain Heights Academy OER |
| Course: | Medical Forensics Q2 |
| Book: | READ: Basic Nervous System Anatomy |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Saturday, 26 July 2025, 9:36 PM |
Introduction
Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Forensic psychology is the study of how a person’s mental state may have been a contributing factor that led them to commit a crime. Before we learn about other aspects of psychology, it is important to have a basic understanding of nervous system anatomy.
Introduction to the Nervous System
Michelle was riding her scooter when she hit a hole in the street and started to lose control. She thought she would fall, but, in the blink of an eye, she shifted her weight and kept her balance. Her heart was pounding, but at least she didn’t get hurt. How was she able to react so quickly? Michelle can thank her nervous system for that ( Figure below ).
Staying balanced when riding a scooter requires control over the body’s muscles. The nervous system controls the muscles and maintains balance.
The nervous system , together with the endocrine system , controls all the other organ systems. The nervous system sends one type of signal around the body, and the endocrine system sends another type of signal around the body. The endocrine system makes and releases chemical messenger molecules, or hormones, which tell other body parts that a change or a reaction is necessary. So what type of signal does the nervous system send?
Controlling muscles and maintaining balance are just two of the roles of the nervous system. The nervous system also lets you:
- Sense your surroundings with your eyes and other sense organs.
- Sense the environment inside of your body, including temperature.
- Control your internal body systems and keep them in balance.
- Prepare your body to fight or flee in an emergency.
- Use language, think, learn, and remember.
The nervous system works by sending and receiving electrical signals. The main organs of the nervous system are the brain and the spinal cord. The signals are carried by nerves in the body, similar to the wires that carry electricity all over a house. The signals travel from all over the body to the spinal cord and up to the brain, as well as moving in the other direction. For example, when Michelle started to fall off her scooter, her nervous system sensed that she was losing her balance. It responded by sending messages from her brain to muscles in her body. Some muscles tightened while others relaxed. Maybe these actions moved her hips or her arms. The nervous system, working together with the muscular and skeletal systems, allowed Michelle to react to the situation. As a result, Michelle’s body became balanced again. The messages released by the nervous system traveled through nerves. Just like the electricity that travels through wires, nerve quickly carry the electrical messages around the body.
Think about how quickly all this happens. It has to be really fast, otherwise Michelle would not have been able to react. What would happen if a car pulled out unexpectedly in front of Michelle? A signal would have to go from her eyes to her brain and then to her muscles. What allows the nervous system to react so fast. It starts with the special cell of the nervous system, the neuron.
Vocabulary
- endocrine system : System of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
- nerve : Bundle of nerve cells.
- nervous system : Body system that sends electrical messages throughout the body; controls all other body systems.
- organ system : Groups of organs that work together to perform a specific task.
Summary
- The nervous system sends electrical messages throughout the body and controls all other body systems.
- The nervous system allows you to think, learn, sense your surroundings, and control your internal body systems.
CK-12 Foundation, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Central Nervous System
The human brain. The "control center." What does it control?
Practically everything. From breathing and heartbeat to reasoning, memory, and language. And it is the main part of the central nervous system.
Central Nervous System
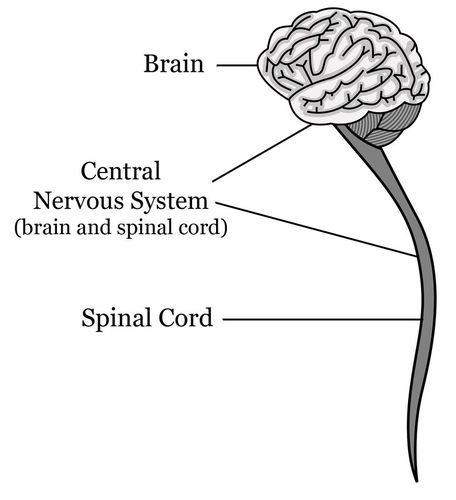
The nervous system has two main divisions: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system (see Figure below ). The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord (see Figure below ).
The two main divisions of the human nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system has additional divisions.
This diagram shows the components of the central nervous system.
CK-12 Foundation, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Brain
The Brain
The brain is the most complex organ of the human body and the control center of the nervous system. It contains an astonishing 100 billion neurons! The brain controls such mental processes as reasoning, imagination, memory, and language. It also interprets information from the senses. In addition, it controls basic physical processes such as breathing and heartbeat.
The brain has three major parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. These parts are shown in Figure below and described in this section.
You can also take an interactive animated tour of the brain:
In this drawing, assume you are looking at the left side of the head. This is how the brain would appear if you could look underneath the skull.
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It controls conscious functions such as reasoning, language, sight, touch, and hearing. It is divided into two hemispheres, or halves. The hemispheres are very similar but not identical to one another. They are connected by a thick bundle of axons deep within the brain. Each hemisphere is further divided into the four lobes shown in Figure below .
- The cerebellum is just below the cerebrum. It coordinates body movements. Many nerve pathways link the cerebellum with motor neurons throughout the body.
- The brain stem is the lowest part of the brain. It connects the rest of the brain with the spinal cord and passes nerve impulses between the brain and spinal cord. It also controls unconscious functions such as heart rate and breathing.
Each hemisphere of the cerebrum consists of four parts, called lobes. Each lobe is associated with particular brain functions. Just one function of each lobe is listed here.
CK-12 Foundation, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem and continues down the center of the back to the pelvis. It is protected by the vertebrae , which encase it. The spinal cord serves as an information superhighway, passing messages from the body to the brain and from the brain to the body.
Summary
- The central nervous includes the brain and spinal cord.
- The brain is the control center of the nervous system. It controls virtually all mental and physical processes.
- The spinal cord is a long, thin bundle of nervous tissue that passes messages from the body to the brain and from the brain to the body.
CK-12 Foundation, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/