EXPLORE: Redshift & Blueshift (BrainPop)
| Site: | Mountain Heights Academy OER |
| Course: | Earth Science Q1 |
| Book: | EXPLORE: Redshift & Blueshift (BrainPop) |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Saturday, 26 July 2025, 2:12 PM |
Description
This book will describe redshift & blueshift. Redshift is one of the pieces of evidence used to support the Big Bang theory.
1. Electromagnetic Spectrum
Because the evidence to support the Big Bang theory deals with radiation, it is important to understand the various forms of radiation in the universe. The collection of all radiation (also known as light and heat), visible and invisible to the naked eye, is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum of light being emitted from stars also tells scientists about the elements that make up the stars.
2. Waves
Light travels in waves, and the changes in the wavelength of light waves can tell scientists about how stars and galaxies are moving relative to us. The following interactive lesson will describe the properties and behaviors of light waves.
3. Redshift & Blueshift
If you look at a star through a prism, you will see a spectrum, or a range of colors through the rainbow. This is just one piece of the electromagnetic spectrum, but changes in this spectrum are one of the key pieces of evidence to support the Big Bang Theory.
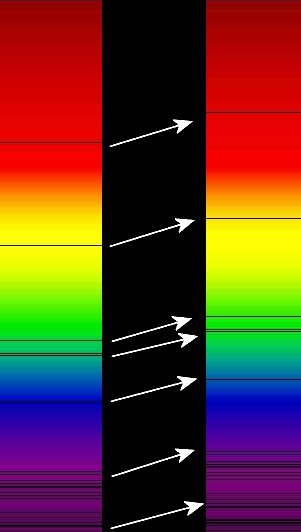
When astronomers started to study the spectrum of light from distant galaxies, they noticed something strange. The dark lines in the spectrum were in the patterns they expected, but they were shifted toward the red end of the spectrum, as shown in the picture below. This shift of absorption bands toward the red end of the spectrum is known as redshift.
Redshift is a shift in absorption bands toward the red end of the spectrum. Redshift occurs when the light source is moving away from you or when the space between you and the source is stretched.
Redshift occurs when the source of light is moving away from the observer. So when astronomers see redshift in the light from a galaxy, they know that the galaxy is moving away from Earth. The strange part is that almost every galaxy in the universe has a redshift, which means that almost every galaxy is moving away from us. This is one piece of evidence astronomers use to support the Big Bang theory because it proves the universe is expanding.
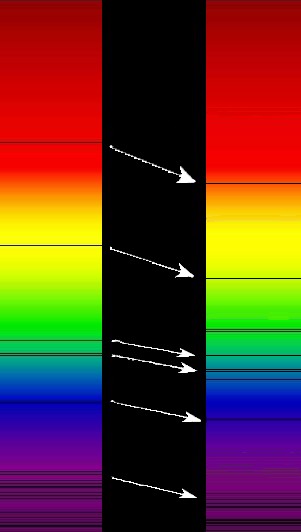
Blueshift is the opposite of redshift. As an object moves towards an observer, the wavelength decreases and light is shifted towards the blue end of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The following video explains redshift and blueshift:
Source
David Bethel
http://ck12.org/flexr/assemble/?fid=732 (CC BY-SA)
4. What Redshift & Blueshift Tell Us
As astronomers observed the stars and made measurements they observed that most nearby galaxies were redshifted. This discovery puzzled scientists, because if the universe was always the same size, then there shouldn't be any shift.
Hubble's discovery that the spectral lines in the light coming from stars undergoes redshift is an important discovery because scientists can estimate distance from the apparent intensity of the stars' light. Hubble noticed that redshift increased with distance; in other words, galaxies farther away from us are moving away from us (and each other) at a higher speed. If galaxies are moving away from each other, then they must have been closer in the past. That means the universe would have been smaller long ago, and has been expanding.
Redshifting in stars and galaxies is one of the key pieces of evidence that scientists use to support the the Big Bang Theory.
5. Doppler Explanation

An analogy to redshift & blueshift is the noise a siren makes as it passes by you. You may have noticed that the siren on an ambulance has a lower pitch after it passes you. The sound waves shift towards a lower pitch when the ambulance speeds away from you because the wavelength is getting longer. The opposite happens when an ambulance is speeding towards you: the pitch gets higher because the sound waves are closer together (in other words, they have a shorter wavelength). The Doppler Effect occurs when the wavelength of waves emanating from a moving source appears to be longer or shorter, depending on whether the object is moving towards or away from the observer.
Though redshift and blueshift involve light waves instead of sound waves, a similar principle operates in both situations. Explore the next interactivity in the course about the Doppler Effect, a change in wavelength caused by the motion of the source. As an object moves away from you, the wavelength increases (redshift). As an object moves towards you, the wavelength decreases (blueshift).