EXPLORE: The Big Bang (BrainPop)
This book will explain the expansion of the universe, and how it led to the Big Bang Theory. It will also describe what happened and what the universe was like right after the Big Bang.
2. The Expanding Universe
The picture below shows a simplified diagram of the expansion of the universe. Another way to picture this is to imagine a balloon covered with tiny dots. Each dot represents a galaxy. When you inflate the balloon, the dots slowly move away from each other because the rubber stretches in the space between them. If it was a giant balloon and you were standing on one of the dots, you would see the other dots moving away from you. Not only that, but dots farther away from you on the balloon would move away faster than dots nearby.
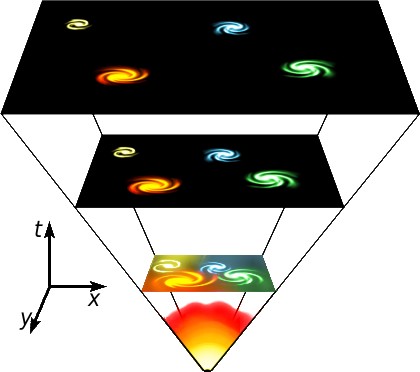
The above is a simplified diagram of the expansion of the universe over time. Note that the distance between galaxies gets bigger as you go forward in time, but the size of each galaxy stays about the same.
An inflating balloon is not exactly like the expanding universe. For one thing, the surface of a balloon has only two dimensions, while space has three dimensions. But it is true that space itself is stretching out between galaxies like the rubber stretches when a balloon is inflated. This stretching of space, which causes the distance between galaxies to increase, is what astronomers mean by the expansion of the universe.
One other difference between the universe and our balloon model involves the actual size of the galaxies. On the inflating balloon, the dots you made will become larger in size as you inflate it. In our universe, however, the galaxies stay the same size; it is just the space between the galaxies that increases as the universe expands.