READ: Analog and Digital Signals
READ: Analog and Digital Signals
Did you ever make a secret code by assigning each letter of the alphabet a unique symbol? The code shown above is believed to have been used by George Washington to send secret messages during the American Revolutionary War. A different type of code can be sent with electric current.
Q: How do you think electric current can be used to encode messages?
A: The short answer is by changing the voltage in an electric circuit. Keep reading to learn more.
Did you know that fireflies talk to each other using light signals from light waves? Firefly lights turn on and off and flash in patterns that are unique. Each blinking pattern is a light signal that helps fireflies communicate.
How do humans communicate over long distances? How does that signal actually get sent and received?
Electronic Messages
Electric devices, such as lights and household appliances, change electric current to other forms of energy. For example, an electric stove changes electric current to thermal energy. Other common devices, such as mobile phones and computers, use electric current for another purpose: to encode information. A message encoded this way is called an electronic signal, and the use of electric current for this purpose is called electronics.
To encode a message with electric current, the voltage is changed rapidly, over and over again. Voltage is a difference in electric potential energy that is needed in order for electric current to flow. There are two different ways voltage can be changed, resulting in two different types of electronic signals, called analog signals and digital signals.
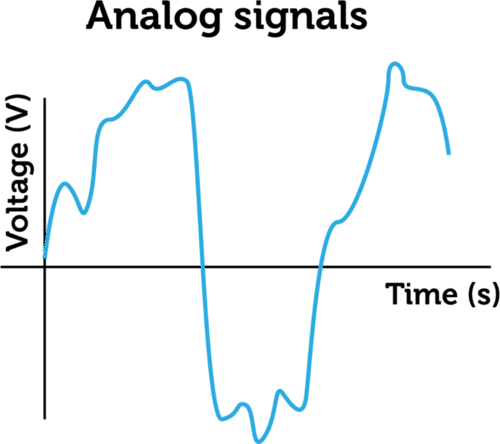
Analog Signals
In the past, before digital technology was invented, people used only analog signals. Analog signals are representations of actual images, sounds, words. They often use waves to transfer information. Analog signals do not use mathematical codes to transfer information. Examples of analog signals are conversations between people which use the sound waves to transfer the information, film cameras which use light waves to imprint the image on the film and vinyl records which use actual waves/grooves in the plastic to make the sound. Some analog signals are simply an instrument used to make a measurement. For example an alcohol thermometer is used for measuring temperatures and a grandfather clock measures time. Can you think of some other examples of analog signals?
Analog signals can also consist of continuously changing voltage in an electric circuit. The figure below represents analog signals. These were the first electronic signals to be invented. They were used in early computers and other early electronic devices. Analog signals are subject to distortion and noise, so they aren’t used as often anymore. They are used mainly in microphones and some mobile phones to encode sounds as electronic signals.
Digital Signals
Today, most electronic signals are digital signals. Digital signals consist of rapid pulses of voltage that repeatedly switch the current off and on. The figure below represents digital signals. This type of signal encodes information as a string of 0’s (current off) and 1’s (current on). This is called a binary (“two-digit”) code. The majority of modern electronic devices, including computers and many mobile phones, encode data as digital signals. Compared with analog signals, digital signals are easier to transmit and more accurate.
Everything that you see or hear on a computer—words, pictures, numbers, movies and sound--uses digital signals. Digital signals are sent as mathematical coded waves and can be sent over long distances. Once the waves arrive at a receiving station, they are decoded back into information that you can understand. In the example of the computer the signal is sent to the speakers which decodes it back into sound or light.
Most of the electronic devices used today, including smartphones, handheld devices, digital thermometers, digital cameras and video game systems, work by transmitting and receiving digital signals in waves.Can you think of other examples of digital signals?
Vocabulary:
- Analog signals are representations of actual images, sounds, words. They often use waves to transfer information.
- Digital signals are sent as mathematical coded waves and can be sent over long distances.
Summary:
- A message encoded by changing the voltage of an electric current is called an electronic signal. The use of electric current for this purpose is known as electronics.
- Electronic signals may be analog or digital signals. Analog signals consist of continuously changing voltage in an electric circuit. Digital signals, which are the main type of signals used today, consist of rapid pulses of voltage that repeatedly switch the current off and on.