READ: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
READ: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Are bacteria cells like our cells?
Yes and no. Bacteria cells are similar to our cells in some ways. Like our cells, bacteria cells have DNA and a plasma membrane. But bacteria are unique in other ways. They are called prokaryotic cells because of these differences.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
There are two basic types of cells, prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. The main difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. The nucleus is where cells store their DNA, which is the genetic material. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Instead, their DNA floats around inside the cell.
Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. All prokaryotes are single-celled organisms. Bacteria and Archaea are the only prokaryotes. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes. All multicellular organisms are eukaryotes. Eukaryotes may also be single-celled.
Eukaryotic Cells
In addition to a nucleus, eukaryotic cells include other membrane-bound structures called organelles. Organelles allow eukaryotic cells to be more specialized than prokaryotic cells. Pictured below are the organelles of eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
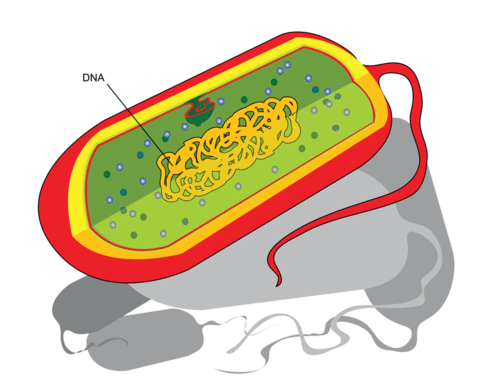
Prokaryotic cells are usually smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells. They do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. In prokaryotic cells, the DNA, or genetic material, forms a single large circle that coils up on itself. The DNA is located in the main part of the cell.
| Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No | Yes |
| DNA | Single circular piece of DNA | Multiple chromosomes |
| Membrane-Bound Organelles | No | Yes |
| Examples | Bacteria | Plants, animals, fungi |
Summary
- All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA.
- Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound structures.
- Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound structures called organelles.