READ: Cell Organelles
READ: Cell Organelles
Do brain cells have the same internal structures as your other cells?
Yes. Although brain cells look quite different from your other cells, they have the same internal structures as other cells. They need the same structures because they need to perform the same tasks, such as making proteins and obtaining energy.
Cell Organelles
Cells are made up of many different parts. Each part has a special role. The different parts of the cell are called organelles, which means "small organs." Some of the major organelles are described below.
The Plasma Membrane
All cells have a barrier around them that separates them from the environment and from other cells. This barrier is called the plasma membrane, or cell membrane.The plasma membrane is made of a double layer of special lipids, known as phospholipids.
Lipids do not mix with water (recall that oil is a lipid), so the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane acts as a barrier, keeping water out of the cell, and keeping the cytoplasm inside the cell. The cell membrane allows the cell to stay structurally intact in its water-based environment.
The function of the plasma membrane is to control what goes in and out of the cell. Some molecules can go through the cell membrane to enter and leave the cell, but some cannot.
Cytosol
The inside of all cells also contain a jelly-like substance called cytosol. Cytosol is composed of water and other molecules. Everything in the cell sits in the cytosol, like fruit in a jello mold. The term cytoplasm refers to the cytosol and all of the organelles. The cytoplasm does not include the nucleus.
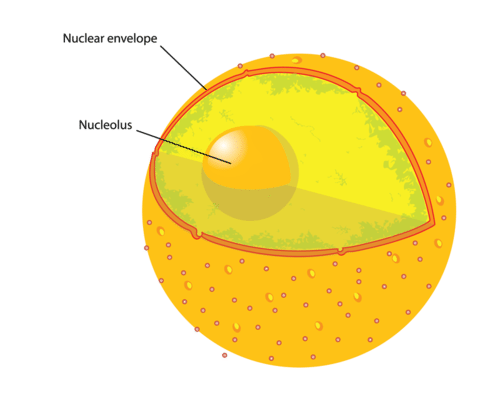
The Nucleus
The nucleus is only found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the genetic material (the DNA) of the cell. The genetic material of the nucleus is like a set of instructions. These instructions tell the cell how to build molecules needed for the cell to function properly. That is, the DNA tells the cell how to build molecules needed for life.
Inside of the nucleus, you will find the chromosomes. Chromosomes are strands of DNA wrapped around proteins. They contain genes, or small units of genetic material (DNA) that contains the code for the creation of a protein.
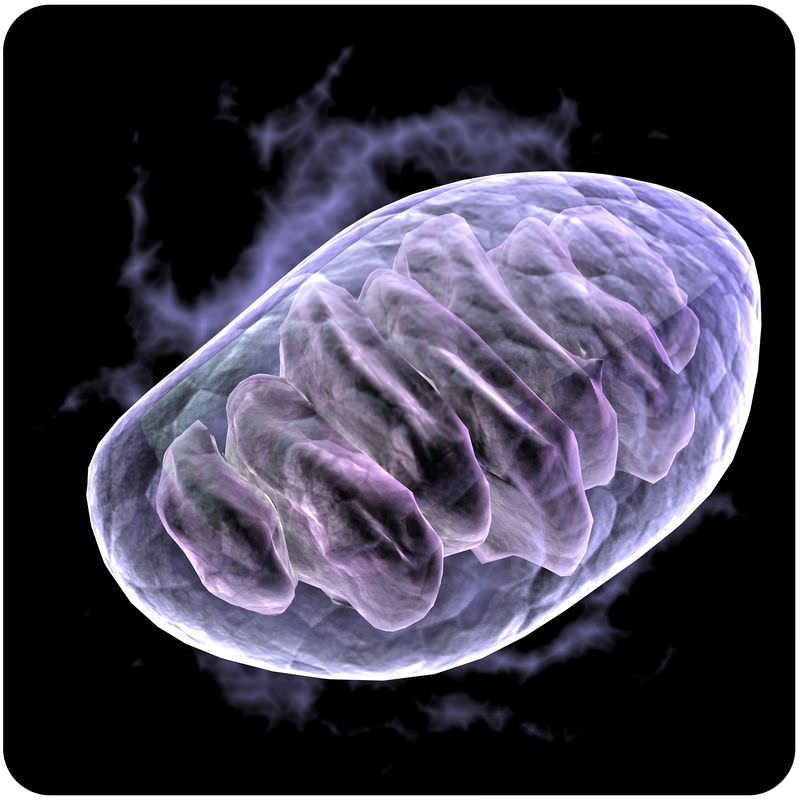
The Mitochondria
A mitochondrion is an organelle that is found in most eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria are called the "power plants" of the cell because they are the sites of cellular respiration, where they use energy from food to make ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is the cell's energy source that is used for such things such as movement and cell division.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles where proteins are made. They are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Summary
- The plasma membrane is formed by a phospholipid bilayer.
- The plasma membrane controls what moves inside and outside the cell.
- The cytosol is the jelly-like material in which the contents of the cell are suspended.
- The nucleus contains the genetic material of the cell.
- The genetic material of the cell is found in chromosomes, DNA wrapped around proteins.
- Ribosomes are small organelles and are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes are found in all cells.
- Mitochondria are where energy from organic compounds is used to make ATP.