READ: Natural Selection
READ: Natural Selection
Darwin's Theory of Evolution
Charles Darwin was one of the most influential scientists who has ever lived. Darwin introduced the world to the theory of evolution by natural selection, which laid the foundation for how we understand the living world today.
Do you ever wonder why some birds are big like ostriches and some birds are small like robins? Or why a lion has a mane while a leopard has spots? In the 19th century, an English natural scientist named Charles Darwin was also fascinated by the diversity of life on Earth.
He set out to answer the following questions:
- Why are organisms different?
- Why are organisms similar?
- Why are there so many different types of organisms?
To answer his questions, he developed what we now call "the theory of evolution by natural selection." This theory is one of the most important theories in the field of life science. In everyday English, "evolution" simply means "change." In biology, evolution states that all living organisms came from earlier forms of life. The theory of evolution by natural selection explains why evolution occurs. Darwin spent over 20 years traveling around the world and making observations before he fully developed his theory.
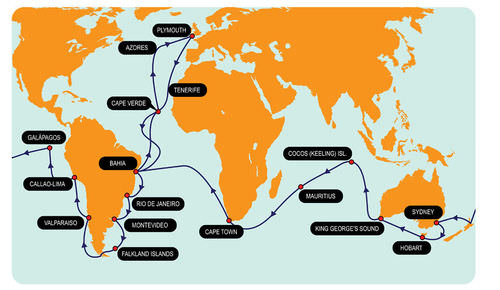
Voyage of the HMS Beagle
In 1859, Charles Darwin published his book, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (often known as The Origin of Species). His book describes the observations and evidence that he collected more than 20 years of research, beginning with a five-year voyage around the world on a British research ship, the HMS Beagle. During the voyage, Darwin made observations about plants and animals around the world. He also collected specimens to study for when he returned to England.
Each time the HMS Beagle stopped at a port, Darwin went on land to explore and look at the local plants, animals, and fossils. One of the most important things Darwin did was keep a diary. He took detailed notes and made drawings of his observations.
Charles Darwin’s famous five year voyage was aboard the HMS Beagle from 1831-1836.
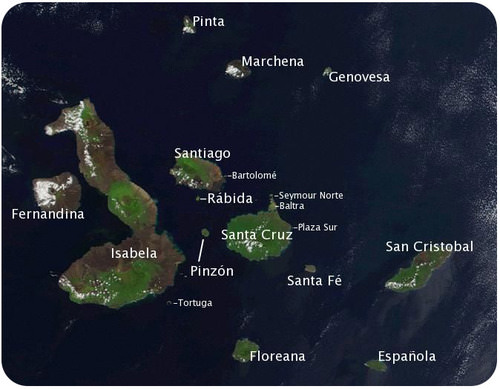
The Galápagos Islands
While the crew of the HMS Beagle mapped the coastline of South America, they traveled to a group of islands called the Galápagos. The Galápagos are a group of 16 volcanic islands near the equator, about 600 miles from the west coast of South America. Darwin spent months on foot exploring the islands. The specimens he collected from the Galápagos and sent back to England greatly influenced his ideas of evolution.
Giant Tortoises
On the Galápagos, Darwin observed that the same kind of animal differed from one island to another. For example, Darwin observed giant tortoises on the Galápagos. He noticed that different tortoise species lived on islands with different environments. He realized that the tortoises had traits that allowed them to live in their particular environments. For example, tortoises that ate plants near the ground had rounded shells and shorter necks. Tortoises on islands with tall shrubs had longer necks and shells that bent upward, allowing them to stretch their necks.
Darwin began to hypothesize that organisms developed traits over time because of differences in their environments. Darwin began to think that organisms evolved adaptations that allowed them to live in their environment. These adaptations were beneficial traits for their environment.
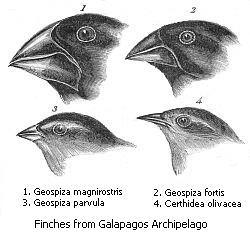
Darwin's Finches
The most studied animals on the Galápagos are finches, a type of bird. When Darwin first observed finches on the islands, he did not even realize they were all finches. But when he studied them further, he realized they were related to each other. Each island had its own distinct species of finch. The birds on different islands had many similarities, but their beaks differed in size and shape.
In his diary, Darwin pointed out how each animal is well-suited for its particular environment. The shapes of the finch beaks on each island were well-matched with the seeds available on that island, but not the seeds on other islands. For example, a larger and stronger beak was needed to break open large seeds on one island, and a small beak was needed to eat the small seeds on a different island.
Natural Selection
The theory of evolution by natural selection means that the inherited traits of a population change over time. Natural selection explains how organisms in a population develop traits that allow them to survive and reproduce. Natural selection means that traits that offer an advantage will most likely be passed on to offspring; individuals with those traits have a better chance of surviving. Evolution occurs by natural selection.
Natural selection occurs when:
- There is some variation in the inherited traits of organisms within a species. Without this variation, natural selection would not be possible.
- Some of these traits will give individuals an advantage over others in surviving and reproducing.
- These individuals will be likely to have more offspring.
Imagine how in the Arctic, dark fur makes a rabbit easy for foxes to spot and catch in the snow. Therefore, white fur is a beneficial trait that improves the chance that a rabbit will survive, reproduce, and pass the trait of white fur on to its offspring. Through this process of natural selection, dark fur rabbits will become uncommon over time. Rabbits will adapt to have white fur. In essence, the selection of rabbits with white fur - the beneficial trait - is a natural process.
The white fur of the Arctic hares may make it more difficult for fox and other predators to locate hares against the white snow.
Why So Many Species?
Scientists estimate that there are between 5 million and 30 million species on the planet. But why are there so many? Different species are well-adapted to live and survive in many different types of environments. As environments change over time, organisms must constantly adapt to those environments. Diversity of species increases the chance that at least some organisms adapt and survive any major changes in the environment. For example, if a natural disaster kills all of the large organisms on the planet, then the small organisms will continue to survive.
Summary
- Charles Darwin developed what we now call "the theory of evolution by natural selection."
- Darwin's observations on the Galápagos Islands suggested that animals are well-suited for their specific environments.
- Evolution occurs by natural selection, the process by which organisms with traits that better enable them to adapt to their environment will tend to survive and reproduce in greater numbers.
- Evolution is due to differences in the survival and reproduction of individuals within a population.
- Natural selection occurs when there is some variation in the inherited traits, some of these traits will give individuals an advantage over others, and the individuals with certain traits will be more likely to have more offspring.