READ: El Nino and La Nina
Completion requirements
El Niño & La Niña
El Niño is a short-term climate phenomenon which lasts for a year or two. It influences sea surface temperatures and ocean currents. These changes in water temperature, winds, and currents affect climates worldwide. The changes usually last a year or two. Some places get more rain than normal. Other places get less. In many locations, the weather is more severe.
During an El Niño, the western Pacific Ocean is warmer than usual. This causes the trade winds to change direction. The winds blow from west to east instead of east to west. The warm water travels east across the equator, too. Warm water piles up along the western coast of South America. Therefore, El Niño years are associated with an increase in flooding in South America, while Indonesia experiences drought conditions.
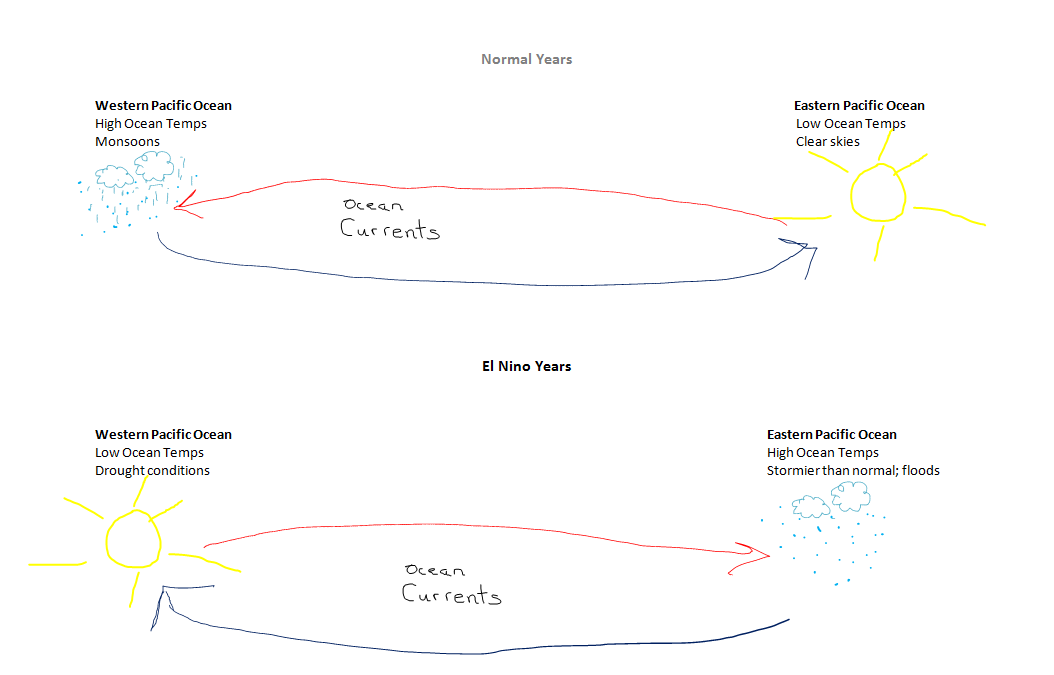
La Niña generally follows El Niño. It occurs when the Pacific Ocean is cooler than normal. The trade winds are like they are in a normal year. They blow from east to west. But in a La Niña the winds are stronger than usual. More cool water builds up in the western Pacific. These changes can also affect climates worldwide.
Source: Climate Change. Retrieved from http://www.ck12.org/section/Climate-Change-%253A%253Aof%253A%253A-MS-Climate/ on August 28, 2013.
After you have completed this part of the lesson, you can check the associated box on the main course page to mark it as complete
Last modified: Monday, 5 January 2015, 12:12 PM